Equity Markets - India & US
Bellwether indices, Nifty 50 and BSE Sensex moved down sharply during the month by 1.38% and 1.69% respectively due to signs of weakening earnings momentum among domestic companies in Q1FY26 and additional 25% tariff imposed by the U.S. President on India which came into effect on Aug 27, 2025. Investor sentiment weakened as the 50% tariff hike threatened India’s manufacturing push and could slow economic growth. Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) net sellers in Indian equities to the tune of ₹ 34993.16 crore. Gross Goods and Services Tax (GST) collections in Aug’25 stood at Rs. 1.86 trillion, representing a 6.5% rise on a yearly basis and this points towards the growing trajectory of the Indian economy. Dow Jones increased by 3.20% from previous month.
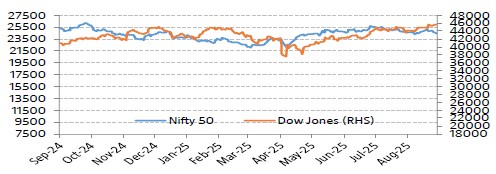
Interest Rate Movement (%) - India & US
Yield on the 10-Year benchmark paper marginally increased, closing at 6.568% on Aug’25 vs 6.374% on Jul’25 as after announcement of sweeping changes to the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, reigniting fiscal concerns and heightening fears of increased debt supply. US 10 year G-Sec closed higher at 4.2284 on Aug’25 vs 4.374 on Jul’25.
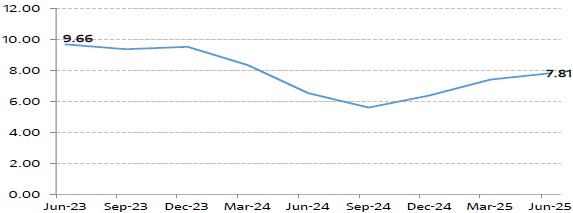
India GDP Growth Rate
India’s GDP grows 7.81% for Q1 FY26 vs 7.38% for Q4 FY25, The robust GDP growth was led by a sharp growth in the manufacturing sector and strong momentum in the services sector. India’s agricultural sector bounced back robustly with a 3.7% growth, manufacturing sector saw an impressive 7.7% growth, while construction grew at 7.6%. Services sector, which includes critical components like trade, hotels, and financial services, growth skyrocketed by 9.3%.